Data observability facilitates and enhances data management strategies. But this should be more than just keeping track of KPIs and putting them on dashboards for analysis. For it to be used in business or technical teams’ enterprise functions, it needs to make a good leap. This includes using advanced approaches to actual business operations data. It will help put observable information into its proper context, which can help leaders take the right steps. This is “Applied Observability,” the approach of transforming observed data into actionable insights for decision-makers in any technological or business domain.
The Applied Observability Concept
“Applied observability” is the process of using observable data across business functions, application teams, and infrastructure teams in a way that is well-coordinated and works well together. This allows for the shortest latency from (stakeholder) action to (organization) reaction, as well as proactive planning of business decisions.
Applied observability is committed to the notion that the future success of any business is not only dependent on predicting the future, but also on carefully planning based on actual data. This is the goal that drives Applied Observability. If businesses are diligent about implementing the idea of “applied observability,” they will be able to cut down on the amount of time it takes them to respond to customers’ inquiries and boost the effectiveness of their day-to-day operations. To see the value of applied observability, you need to switch from being reactive to being proactive. The key to getting a competitive edge is for IT leaders to be able to use the actual actions of stakeholders instead of their intentions or educated guesses.
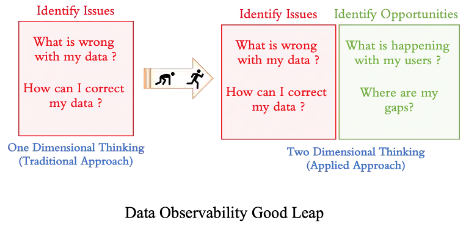
As illustrated in the graphic above, I believe our original concept about Data Observability necessitates a good leap. From a traditional standpoint, we regard data observability as a tool for simply identifying issues that signal anything incorrect with the present data. This prompts us to consider what automated or manual steps can be made to resolve those problems. This is a one-dimensional technique in the classic sense. When you consider how to convert observable data into actionable insights as quickly as possible for business success, this becomes an opportunity. This adds another dimension to Data Observability by recognizing opportunities that lead to business expansions. It looks at addressing questions about what is going on with my customers and whether there are any gaps in my business that need to be filled. When we understand and implement Data Observability as a two-dimensional axis, we can term this an applied approach to Data Observability, or “Applied Observability.”
Applied observability enables businesses to compete by leveraging data artifacts. Using data from previous system expenditures, the organization creates digital customer value at no marginal cost. Applied observability is hard and time-consuming. To succeed, functional business groups must collaborate. focuses on stakeholder actions rather than intentions. At Atgeir Solutions, we are building DataGeir™ HawkEye™ with the vision of “Establishing Trust By Enabling Transparency”. The product takes a two-dimensional approach to Data Observability in order to suit the needs of Applied Observability. It helps you capture, monitor, debug, manage, and apply observable data across domains spanning from technical to business processes.
I hope this article clarifies the concept of “Applied Observability”. Take pleasure in observing your organization’s data and using it to expand your business.
Originally posted on Medium : https://medium.com/@1704.manish/applied-observability-the-new-approach-1e36cd592b20
